Accessing Milton
Last updated on 2025-09-03 | Edit this page
Estimated time: 21 minutes
Overview
Questions
- How do I log in to
Milton? - Where can I store my data?
Objectives
- Connect to
Milton. - Identify where to save your data
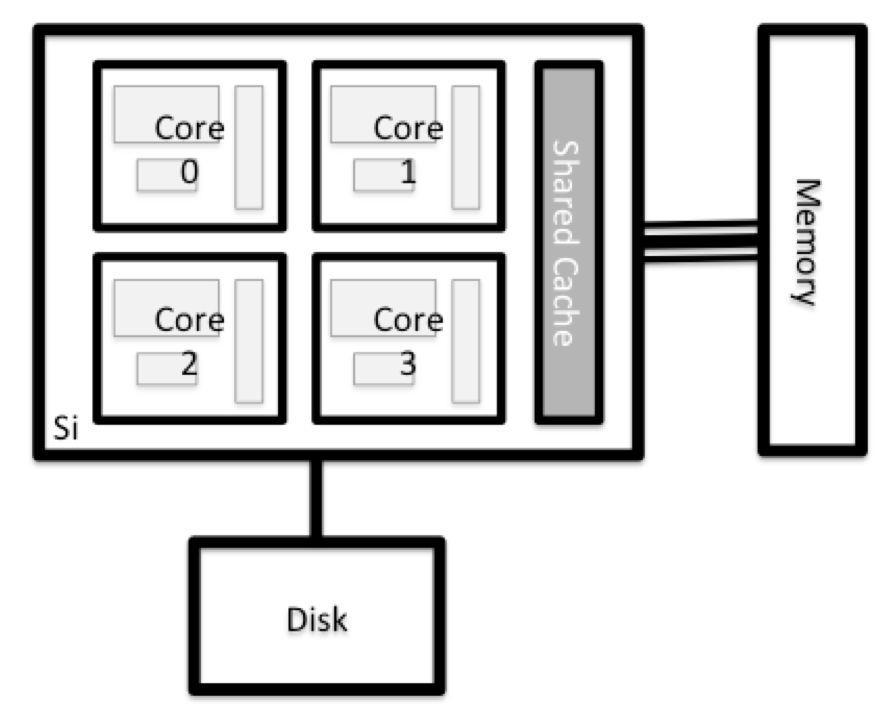
Milton Cluster
Milton is a linux-based cluster, that is made up of two login nodes and many computer nodes in addition to the file systems.
Connect to Milton
The first step in using a cluster is to establish a connection from your laptop to the cluster. You need a Windows Command Prompt or macOS Terminal, to connect to a login node and access the command line interface (CLI).
Exercise 1: Can you login to Milton?
If not in WEHI, make sure you are on the VPN. While on a WEHI device, open your terminal and login to slurm-login.
More details are available here.
- For Mac OSX users
ssh slurm-login- Type your password
- For MS-Windows users
- Download and install the free GitBash app.
- You can also use Cluster Access on Open OnDemand
You will be asked for your password.
Watch out: the characters you type after the
password prompt are not displayed on the screen. Normal output will
resume once you press Enter.
You will notice that the prompt changed when you logged into the remote system using the terminal.
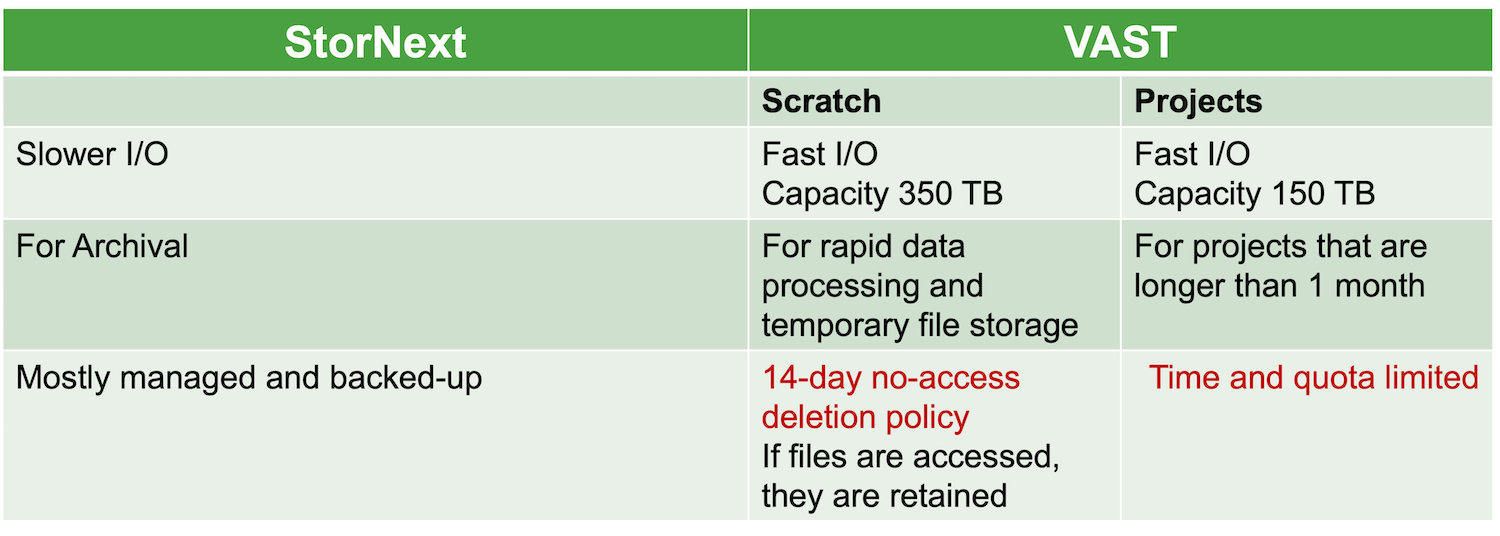
Milton File Systems
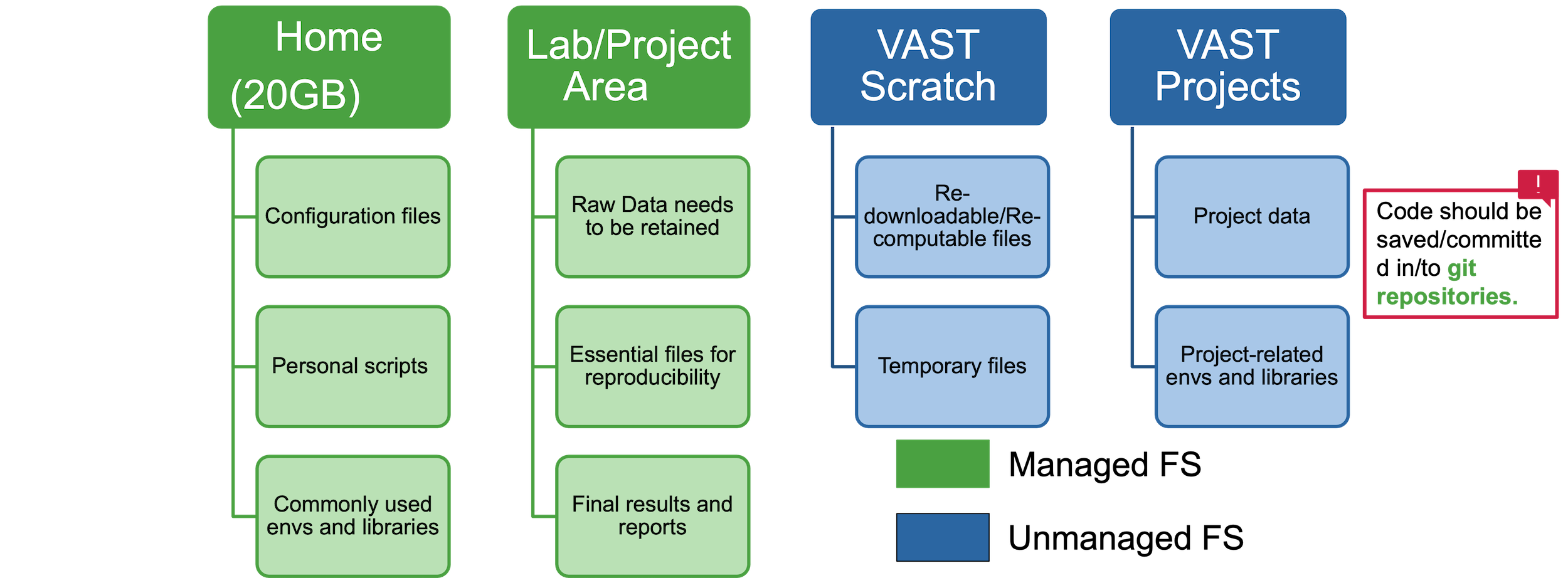
How data should be moved between file systems according to project requirements?
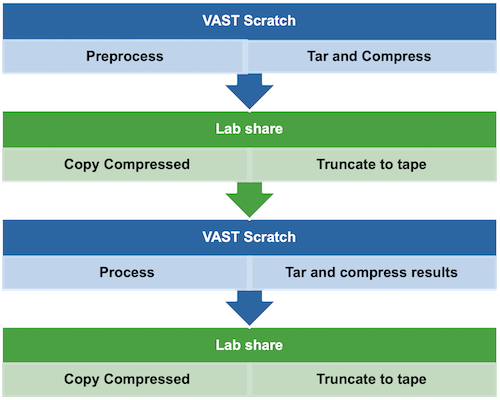
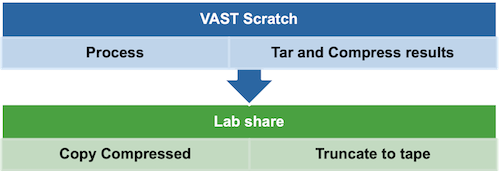
Check your available storage
Use module av to search for and load the
stornext module. Load it and run the mrquota
tool to view your available storage.
Check your available storage (continued)
Looks like my home dir is nearly full!
Looking Around Your Home
We will now revise some linux commands to look around the login node.
Exercise 2:Check the name of the current node
Get node name where you are logged into
Exercise 3: Find out which directory we are in.
Exercise 4: List all files and folders in your Home directory
Exercise 5: Copy Exercise examples to your vast scratch or home directory
Copy exercise examples from Github to current directory,
Exercise 6: Disconnect your session
For more on Linux commands, visit our guide or watch the recording of the workshops here
- HPC systems typically provide login nodes and a set of compute nodes.
- Files saved on one node are available on all nodes.
- Milton has multiple different file systems that have different policies and characteristics.
- Throughout a research project, research data may move between file systems according to backup and retention requirements, and to improve performance.